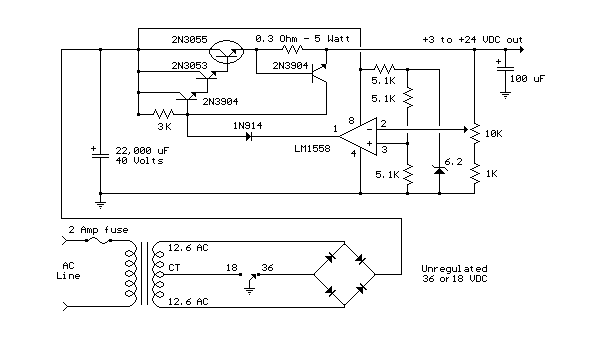
Схема блока питания с регулируемым питанием на выходе от 3 до 24 Вольт на 3 Ампера.
This regulated power supply can be adjusted from 3 to 25 volts and is current limited to 2 amps as shown, but may be increased to 3 amps or more by selecting a smaller current sense resistor (0.3 ohm). The 2N3055 and 2N3053 transistors should be mounted on suitable heat sinks and the current sense resistor should be rated at 3 watts or more. Voltage regulation is controlled by 1/2 of a 1558 or 1458 op-amp. The 1458 may be substituted in the circuit below, but it is recommended the supply voltage to pin 8 be limited to 30 VDC, which can be accomplished by adding a 6.2 volt zener or 5.1 K resistor in series with pin 8. The maximum DC supply voltage for the 1458 and 1558 is 36 and 44 respectively. The power transformer should be capable of the desired current while maintaining an input voltage at least 4 volts higher than the desired output, but not exceeding the maximum supply voltage of the op-amp under minimal load conditions. The power transformer shown is a center tapped 25.2 volt AC / 2 amp unit that will provide regulated outputs of 24 volts at 0.7 amps, 15 volts at 2 amps, or 6 volts at 3 amps. The 3 amp output is obtained using the center tap of the transformer with the switch in the 18 volt position. All components should be available at Radio Shack with the exception of the 1558 op-amp.
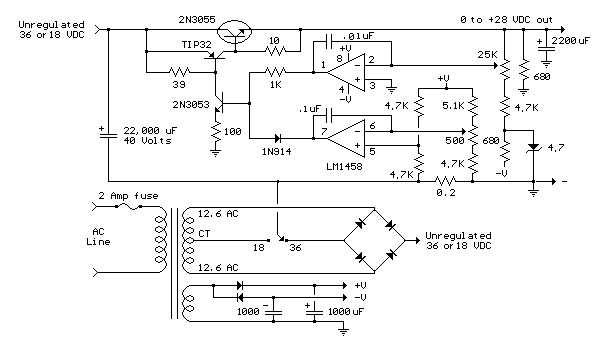
Схема регулируемого блока питания (0-28 Вольт)
Another method of using opamps to regulate a power supply is shown below. The power transformer requires an additional winding to supply the op-amps with a bipolar voltage (+/- 8 volts), and the negative voltage is also used to generate a reference voltage below ground so that the output voltage can be adjusted all the way down to 0. Current limiting is accomplished by sensing the voltage drop across a small resistor placed in series with the negative supply line. As the current increases, the voltage at the wiper of the 500 ohm pot rises until it becomes equal or slightly more positive than the voltage at the (+) input of the opamp. The opamp output then moves negative and reduces the voltage at the base of the 2N3053 transistor which in turn reduces the current to the 2N3055 pass transistor so that the current stays at a constant level even if the supply is shorted. Current limiting range is about 0 — 3 amps with components shown. The TIP32 and 2N3055 pass transistors should be mounted on suitable heat sinks and the 0.2 ohm current sensing resistor should be rated at 2 watts or more. The heat produced by the pass transistor will be the product of the difference in voltage between the input and output, and the load current. So, for example if the input voltage (at the collector of the pass transistor) is 25 and the output is adjusted for 6 volts and the load is drawing 1 amp, the heat dissipated by the pass transistor would be (25-6) * 1 = 19 watts. In the circuit below, the switch could be set to the 18 volt position to reduce the heat generated to about 12 watts.
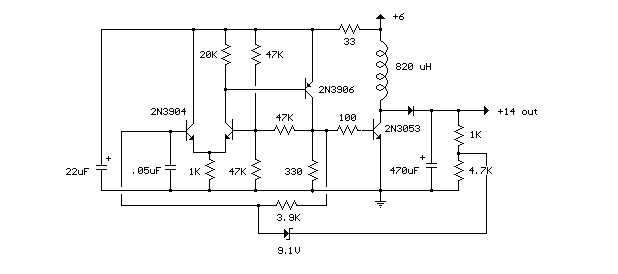
Схема преобразователя напряжения (2 Ватт)
In this small switching power supply, a Schmitt trigger oscillator is used to drive a switching transistor that supplies current to a small inductor. Energy is stored in the inductor while the transistor is on, and released into the load circuit when the transistor switches off. The output voltage is dependent on the load resistance and is limited by a zener diode that stops the oscillator when the voltage reaches about 14 volts. Higher or lower voltages can be obtained by adjusting the voltage divider that feeds the zener diode. The efficiency is about 80% using a high Q inductor.
© Kruso.su 2009 - 2021 Все права защищены